Requests
Creating and managing HTTP requests in Yasumu.
Requests
Requests are the core building blocks of API testing in Yasumu. This guide covers creating, configuring, and organizing HTTP requests.
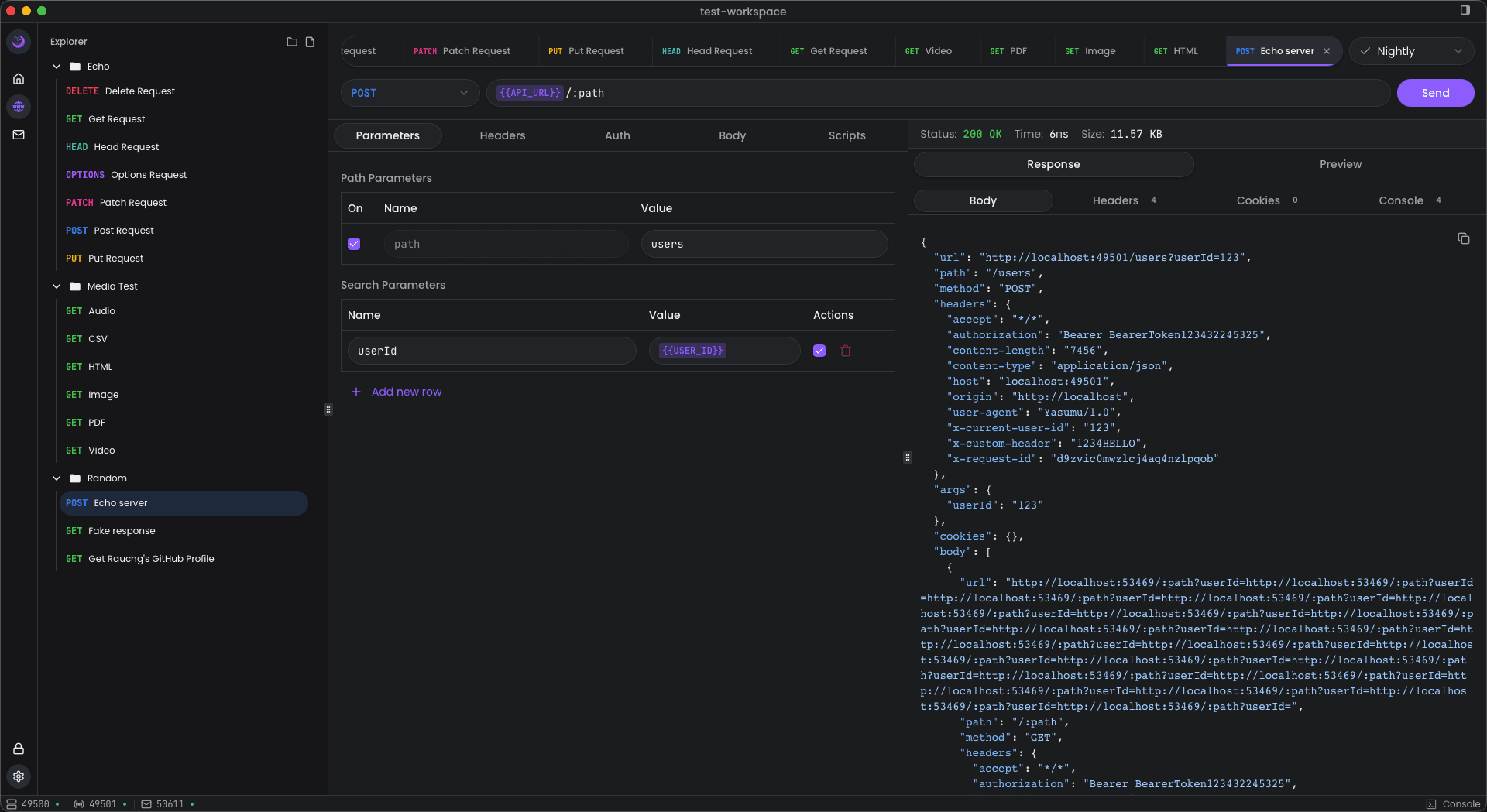
Creating a Request
To create a new request:
- Navigate to the REST section in the sidebar
- Click the + button or use the context menu
- Configure the request details in the editor
Request File Structure
Each request in Yasumu is stored as a .ysl file with the following
structure:
@rest
metadata {
name: "Echo"
method: "GET"
id: "wmz1pu98ovohr1k44dbldpjt"
groupId: "xpm4mym1hqvcqq3fqc0hppv1"
}
request {
url: "{{API_URL}}/?apiKey={{API_KEY}}"
headers: []
body: null
}
dependencies []File Naming
Request files are named using unique IDs (e.g.,
wmz1pu98ovohr1k44dbldpjt.ysl). The human-readable name is stored in
the metadata.name field.
Metadata Block
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
name | Display name in the UI |
method | HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, etc.) |
id | Unique identifier for the request |
groupId | ID of the group this request belongs to (optional) |
Request Block
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
url | Request URL (supports variables) |
headers | Array of request headers |
body | Request body (null for GET requests) |
HTTP Methods
Yasumu supports all standard HTTP methods:
- GET — Retrieve data
- POST — Create new resources
- PUT — Update/replace resources
- PATCH — Partial updates
- DELETE — Remove resources
- HEAD — Headers only
- OPTIONS — CORS preflight
Variables
Use double curly braces to reference variables in URLs and headers:
url: "{{API_URL}}/users/{{userId}}"Variables are resolved from:
- Environment variables — From the active environment
- Environment secrets — Secret values from the active environment
Variable Resolution
Variables are resolved at request time from the currently active environment.
Headers
Headers are stored as an array in the request block:
headers: [
{ key: "Content-Type", value: "application/json", enabled: true },
{ key: "Authorization", value: "Bearer {{API_KEY}}", enabled: true }
]Each header has:
key— Header namevalue— Header value (supports variables)enabled— Whether the header is active
Request Body
The body can be:
null— No body (typical for GET requests)- JSON object — For POST, PUT, PATCH requests
Response Handling
After sending a request, Yasumu displays:
- Status Code — HTTP response status
- Response Time — Duration of the request
- Size — Response payload size
- Headers — Response headers
- Body — Response body with syntax highlighting
Response Formats
Yasumu automatically formats common response types:
- JSON — Pretty-printed with syntax highlighting
- XML — Formatted and highlighted
- HTML — Rendered or source view
- Plain Text — As-is display
Request Groups
Requests can be organized into groups using the groupId field.
Groups are defined in the workspace configuration and help organize
related requests.
Dependencies
The dependencies array allows you to define requests that should run
before this request:
dependencies ["wmz1pu98ovohr1k44dbldpjt"]Best Practices
- Use descriptive names — Give requests clear, descriptive names in the metadata
- Use variables — Avoid hardcoding URLs and credentials
- Organize with groups — Group related requests together
- Version your requests — Commit changes to version control
